Servers - IIS - Troubleshoot
In this article
App startup errors
403.14 Forbidden
-
The app is deployed to the wrong folder on the hosting system.
-
The deployment process failed to move all of the app's files and folders to the deployment folder on the hosting system.
-
The web.config file is missing from the deployment, or the web.config file contents are malformed.
-
Delete all of the files and folders from the deployment folder on the hosting system.
-
Redeploy the contents of the app's publish folder to the hosting system using your normal method of deployment, such as Visual Studio, PowerShell, or manual deployment:
-
Confirm that the web.config file is present in the deployment and that its contents are correct.
-
When hosting on Azure App Service, confirm that the app is deployed to the
D:\home\site\wwwrootfolder. -
When the app is hosted by IIS, confirm that the app is deployed to the IIS Physical path shown in IIS Manager's Basic Settings.
-
-
Confirm that all of the app's files and folders are deployed by comparing the deployment on the hosting system to the contents of the project's publish folder.
500 Internal Server Error
500.0 In-Process Handler Load Failure
-
Contact Microsoft Support (select Developer Tools then ASP.NET Core).
-
Ask a question on Stack Overflow.
-
File an issue on our GitHub repository.
500.30 In-Process Startup Failure
-
The app is misconfigured due to targeting a version of the ASP.NET Core shared framework that isn't present. Check which versions of the ASP.NET Core shared framework are installed on the target machine.
-
Using Azure Key Vault, lack of permissions to the Key Vault. Check the access policies in the targeted Key Vault to ensure that the correct permissions are granted.
500.31 ANCM Failed to Find Native Dependencies
-
Install the appropriate version of .NET Core on the machine.
-
Change the app to target a version of .NET Core that's present on the machine.
-
Publish the app as a self-contained deployment.
500.32 ANCM Failed to Load dll
-
Republish the app for the same processor architecture as the worker process.
-
Publish the app as a framework-dependent deployment.
500.33 ANCM Request Handler Load Failure
500.34 ANCM Mixed Hosting Models Not Supported
500.35 ANCM Multiple In-Process Applications in same Process
500.36 ANCM Out-Of-Process Handler Load Failure
500.37 ANCM Failed to Start Within Startup Time Limit
500.38 ANCM Application DLL Not Found
-
Disable single-file publishing by setting the
PublishSingleFileMSBuild property tofalse. -
Switch to the out-of-process hosting model by setting the
AspNetCoreHostingModelMSBuild property toOutOfProcess.
502.5 Process Failure
Failed to start application (ErrorCode '0x800700c1')
-
Select the app pool in IIS Manager's Application Pools.
-
Select Advanced Settings under Edit Application Pool in the Actions panel.
-
Set Enable 32-Bit Applications:
-
If deploying a 32-bit (x86) app, set the value to
True. -
If deploying a 64-bit (x64) app, set the value to
False.
-
Failed to start application (ErrorCode '0x800701b1')
sc.exe start null
Connection reset
Default startup limits
Troubleshoot on Azure App Service
Important ASP.NET Core preview releases with Azure App Service ASP.NET Core preview releases aren't deployed to Azure App Service by default. To host an app that uses an ASP.NET Core preview release, see Deploy ASP.NET Core preview release to Azure App Service.
Azure App Services Log stream
-
In the Azure portal, open the app in App Services.
-
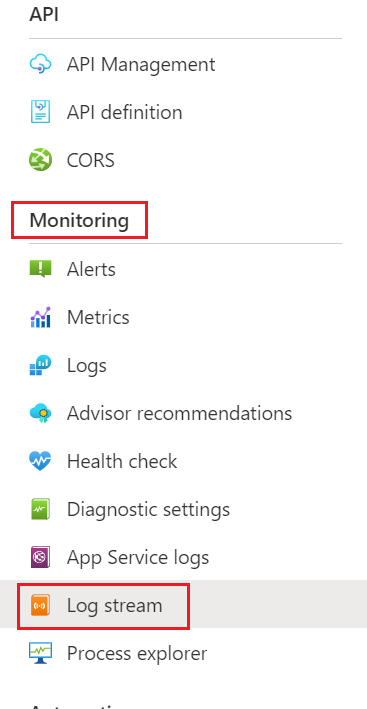
In the left pane, navigate to Monitoring > App Service Logs.

- Select File System for Web Server Logging. Optionally enable Application logging.
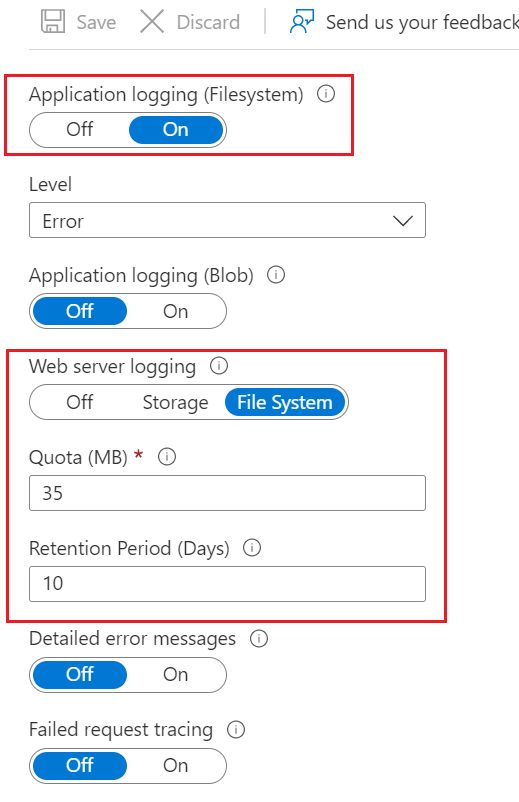
- In the left pane, navigate to Monitoring > Log stream, and then select Application logs or Web Server Logs.

Application Event Log (Azure App Service)
-
In the Azure portal, open the app in App Services.
-
Select Diagnose and solve problems.
-
Select the Diagnostic Tools heading.
-
Under Support Tools, select the Application Events button.
-
Examine the latest error provided by the IIS AspNetCoreModule or IIS AspNetCoreModule V2 entry in the Source column.
-
Open Advanced Tools in the
DevelopmentTools area. Select the Go→ button. The Kudu console opens in a new browser tab or window. -
Using the navigation bar at the top of the page, open Debug console and select CMD.
-
Open the LogFiles folder.
-
Select the pencil icon next to the
eventlog.xmlfile. -
Examine the log. Scroll to the bottom of the log to see the most recent events.
Run the app in the Kudu console
-
Open Advanced Tools in the
DevelopmentTools area. Select the Go→ button. The Kudu console opens in a new browser tab or window. -
Using the navigation bar at the top of the page, open Debug console and select CMD.
Test a 32-bit (x86) app
-
cd d:\home\site\wwwroot -
Run the app:
- If the app is a framework-dependent deployment: dotnet .{ASSEMBLY NAME}.dll
dotnet .\{ASSEMBLY NAME}.dll
- If the app is a self-contained deployment: {ASSEMBLY NAME}.exe
{ASSEMBLY NAME}.exe
-
cd D:\home\SiteExtensions\AspNetCoreRuntime.{X.Y}.x32({X.Y} is the runtime version) -
Run the app:
dotnet \home\site\wwwroot\{ASSEMBLY NAME}.dll
Test a 64-bit (x64) app
- If the app is a 64-bit (x64) framework-dependent deployment:
cd D:\Program Files\dotnet
Run the app: dotnet \home\site\wwwroot\{ASSEMBLY NAME}.dll
-
cd D:\Program Files\dotnet -
Run the app:
dotnet \home\site\wwwroot\{ASSEMBLY NAME}.dll -
If the app is a self-contained deployment:
cd D:\home\site\wwwroot
Run the app: {ASSEMBLY NAME}.exe
-
cdD:\home\site\wwwroot`````` -
Run the app:
{ASSEMBLY NAME}.exe -
cd D:\home\SiteExtensions\AspNetCoreRuntime.{X.Y}.x64({X.Y} is the runtime version) -
Run the app:
dotnet \home\site\wwwroot\{ASSEMBLY NAME}.dll
ASP.NET Core Module stdout log (Azure App Service)
Warning Failure to disable the
stdoutlog can lead to app or server failure. There's no limit on log file size or the number of log files created. Only usestdoutlogging to troubleshoot app startup problems. For general logging in an ASP.NET Core app after startup, use a logging library that limits log file size and rotates logs. For more information, see third-party logging providers.
-
In the Azure Portal, navigate to the web app.
-
In the App Service blade, enter kudu in the search box.
-
Select Advanced Tools > Go.
-
Select Debug console > CMD.
-
Navigate to site/wwwroot
-
Select the pencil icon to edit the web.config file.
-
In the
element, set stdoutLogEnabled="true" and select Save.
ASP.NET Core Module debug log (Azure App Service)
-
To enable the enhanced diagnostic log, perform either of the following:
-
Follow the instructions in Enhanced diagnostic logs to configure the app for an enhanced diagnostic logging. Redeploy the app.
-
Add the
shown in Enhanced diagnostic logs to the live app's web.config file using the Kudu console:
-
Open Advanced Tools in the Development Tools area. Select the Go→ button. The Kudu console opens in a new browser tab or window.
Using the navigation bar at the top of the page, open Debug console and select CMD.
Open the folders to the path site > wwwroot. Edit the web.config file by selecting the pencil button. Add the
- Open Advanced Tools in the ```Development``` Tools area. Select the Go→ button. The Kudu console opens in a new browser tab or window.
- Using the navigation bar at the top of the page, open Debug console and select CMD.
- Open the folders to the path site > wwwroot. Edit the web.config file by selecting the pencil button. Add the <handlerSettings> section as shown in Enhanced diagnostic logs. Select the Save button.
-
Open Advanced Tools in the
DevelopmentTools area. Select the Go→ button. The Kudu console opens in a new browser tab or window. -
Using the navigation bar at the top of the page, open Debug console and select CMD.
-
Open the folders to the path site > wwwroot. If you didn't supply a path for the aspnetcore-debug.log file, the file appears in the list. If you supplied a path, navigate to the location of the log file.
-
Open the log file with the pencil button next to the file name.
-
Remove the
from the web.config file locally and redeploy the app. -
Use the Kudu console to edit the web.config file and remove the
section. Save the file.
Warning Failure to disable the debug log can lead to app or server failure. There's no limit on log file size. Only use debug logging to troubleshoot app startup problems. For general logging in an ASP.NET Core app after startup, use a logging library that limits log file size and rotates logs. For more information, see third-party logging providers.
Slow or hanging app (Azure App Service)
Monitoring blades
-
In the DEVELOPMENT TOOLS blade section, select the Extensions blade.
-
The ASP.NET Core Extensions should appear in the list.
-
If the extensions aren't installed, select the Add button.
-
Choose the ASP.NET Core Extensions from the list.
-
Select OK to accept the legal terms.
-
Select OK on the Add extension blade.
-
An informational pop-up message indicates when the extensions are successfully installed.
-
In the Azure portal, select the Advanced Tools blade in the DEVELOPMENT TOOLS area. Select the Go→ button. The Kudu console opens in a new browser tab or window.
-
Using the navigation bar at the top of the page, open Debug console and select CMD.
-
Open the folders to the path site > wwwroot and scroll down to reveal the web.config file at the bottom of the list.
-
Click the pencil icon next to the web.config file.
-
Set stdoutLogEnabled to
trueand change the stdoutLogFile path to:\\?\%home%\LogFiles\stdout. -
Select Save to save the updated web.config file.
-
In the Azure portal, select the Diagnostics logs blade.
-
Select the On switch for Application Logging (Filesystem) and Detailed error messages. Select the Save button at the top of the blade.
-
To include failed request tracing, also known as Failed Request Event Buffering (FREB) logging, select the On switch for Failed request tracing.
-
Select the Log stream blade, which is listed immediately under the Diagnostics logs blade in the portal.
-
Make a request to the app.
-
Within the log stream data, the cause of the error is indicated.
-
Navigate to the Diagnose and solve problems blade in the Azure portal.
-
Select Failed Request Tracing Logs from the SUPPORT TOOLS area of the sidebar.
Warning Failure to disable the
stdoutlog can lead to app or server failure. There's no limit on log file size or the number of log files created. For routine logging in an ASP.NET Core app, use a logging library that limits log file size and rotates logs. For more information, see third-party logging providers.
Troubleshoot on IIS
Application Event Log (IIS)
-
Open the Start menu, search for Event Viewer, and select the Event Viewer app.
-
In Event Viewer, open the Windows Logs node.
-
Select Application to open the Application Event Log.
-
Search for errors associated with the failing app. Errors have a value of IIS AspNetCore Module or IIS Express AspNetCore Module in the Source column.
Run the app at a command prompt
Framework-dependent deployment
-
At a command prompt, navigate to the deployment folder and run the app by executing the app's assembly with dotnet.exe. In the following command, substitute the name of the app's assembly for <assembly_name>:
dotnet .\<assembly_name>.dll. -
The console output from the app, showing any errors, is written to the console window.
-
If the errors occur when making a request to the app, make a request to the host and port where Kestrel listens. Using the default host and post, make a request to http://localhost:5000/. If the app responds normally at the Kestrel endpoint address, the problem is more likely related to the hosting configuration and less likely within the app.
Self-contained deployment
-
At a command prompt, navigate to the deployment folder and run the app's executable. In the following command, substitute the name of the app's assembly for <assembly_name>:
<assembly_name>.exe. -
The console output from the app, showing any errors, is written to the console window.
-
If the errors occur when making a request to the app, make a request to the host and port where Kestrel listens. Using the default host and post, make a request to http://localhost:5000/. If the app responds normally at the Kestrel endpoint address, the problem is more likely related to the hosting configuration and less likely within the app.
ASP.NET Core Module stdout log (IIS)
-
Navigate to the site's deployment folder on the hosting system.
-
If the logs folder isn't present, create the folder. For instructions on how to enable MSBuild to create the logs folder in the deployment automatically, see the Directory structure topic.
-
Edit the web.config file. Set stdoutLogEnabled to
trueand change the stdoutLogFile path to point to the logs folder (for example,.\logs\stdout).stdoutin the path is the log file name prefix. A timestamp, process id, and file extension are added automatically when the log is created. Usingstdoutas the file name prefix, a typical log file is named stdout_20180205184032_5412.log. -
Ensure your application pool's identity has write permissions to the logs folder.
-
Save the updated web.config file.
-
Make a request to the app.
-
Navigate to the logs folder. Find and open the most recent
stdoutlog. -
Study the log for errors.
-
Edit the web.config file.
-
Set stdoutLogEnabled to
false. -
Save the file.
Warning Failure to disable the
stdoutlog can lead to app or server failure. There's no limit on log file size or the number of log files created. For routine logging in an ASP.NET Core app, use a logging library that limits log file size and rotates logs. For more information, see third-party logging providers.
ASP.NET Core Module debug log (IIS)
<aspNetCore ...>
<handlerSettings>
<handlerSetting name="debugLevel" value="file" />
<handlerSetting name="debugFile" value="c:\temp\ancm.log" />
</handlerSettings>
</aspNetCore>
Enable the Developer Exception Page
<aspNetCore processPath="dotnet"
arguments=".\MyApp.dll"
stdoutLogEnabled="false"
stdoutLogFile=".\logs\stdout"
hostingModel="InProcess">
<environmentVariables>
<environmentVariable name="ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT" value="Development" />
</environmentVariables>
</aspNetCore>
Obtain data from an app
Slow or hanging app (IIS)
App crashes or encounters an exception
-
Create a folder to hold crash dump files at
c:\dumps. The app pool must have write access to the folder. -
Run the EnableDumps PowerShell script:
- If the app uses the in-process hosting model, run the script for w3wp.exe:
.\EnableDumps w3wp.exe
c:\dumps
- If the app uses the in-process hosting model, run the script for w3wp.exe:
.\EnableDumps w3wp.exe
.\EnableDumps w3wp.exe c:\dumps
- If the app uses the out-of-process hosting model, run the script for dotnet.exe:
.\EnableDumps dotnet.exe
c:\dumps
.\EnableDumps dotnet.exe c:\dumps
-
Run the app under the conditions that cause the crash to occur.
-
After the crash has occurred, run the DisableDumps PowerShell script:
- If the app uses the in-process hosting model, run the script for w3wp.exe: .\DisableDumps w3wp.exe
.\DisableDumps w3wp.exe
- If the app uses the out-of-process hosting model, run the script for dotnet.exe: .\DisableDumps dotnet.exe
.\DisableDumps dotnet.exe
Warning Crash dumps might take up a large amount of disk space (up to several gigabytes each).
App hangs, fails during startup, or runs normally
Analyze the dump
Clear package caches
-
Delete the bin and obj folders.
-
Clear the package caches by executing dotnet nuget locals all --clear from a command shell. Clearing package caches can also be accomplished with the nuget.exe tool and executing the command
nuget locals all -clear. nuget.exe isn't a bundled install with the Windows desktop operating system and must be obtained separately from the NuGet website. -
Restore and rebuild the project.
-
Delete all of the files in the deployment folder on the server prior to redeploying the app.
Additional resources
-
Debug .NET and ASP.NET Core source code with Visual Studio
-
Troubleshoot and debug ASP.NET Core projects
-
Common error troubleshooting for Azure App Service and IIS with ASP.NET Core
-
Handle errors in ASP.NET Core
-
ASP.NET Core Module (ANCM) for IIS
Azure documentation
-
Application Insights for ASP.NET Core
-
Remote debugging web apps section of Troubleshoot a web app in Azure App Service using Visual Studio
-
Azure App Service diagnostics overview
-
How to: Monitor Apps in Azure App Service
-
Troubleshoot a web app in Azure App Service using Visual Studio
-
Troubleshoot HTTP errors of "502 bad gateway" and "503 service unavailable" in your Azure web apps
-
Troubleshoot slow web app performance issues in Azure App Service
-
Application performance FAQs for Web Apps in Azure
-
Azure Web App sandbox (App Service runtime execution limitations)
Visual Studio documentation
-
Remote Debug ASP.NET Core on IIS in Azure in Visual Studio 2017
-
Remote Debug ASP.NET Core on a Remote IIS Computer in Visual Studio 2017
-
Learn to debug using Visual Studio
Visual Studio Code documentation
- Debugging with Visual Studio Code