Servers - IIS - In-process hosting
In this article
Enable in-process hosting
<PropertyGroup>
<AspNetCoreHostingModel>InProcess</AspNetCoreHostingModel>
</PropertyGroup>
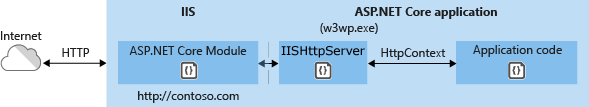
General architecture
-
A request arrives from the web to the kernel-mode HTTP.sys driver.
-
The driver routes the native request to IIS on the website's configured port, usually 80 (HTTP) or 443 (HTTPS).
-
The ASP.NET Core Module receives the native request and passes it to IIS HTTP Server (IISHttpServer). IIS HTTP Server is an in-process server implementation for IIS that converts the request from native to managed.
-
The request is sent to the ASP.NET Core middleware pipeline.
-
The middleware pipeline handles the request and passes it on as an
HttpContextinstance to the app's logic. -
The app's response is passed back to IIS through IIS HTTP Server.
-
IIS sends the response to the client that initiated the request.
Application configuration
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Server.IIS;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using RPauth.Data;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
var connectionString = builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection");
builder.Services.AddDbContext<ApplicationDbContext>(options =>
options.UseSqlServer(connectionString));
builder.Services.AddDatabaseDeveloperPageExceptionFilter();
builder.Services.AddDefaultIdentity<IdentityUser>(options => options.SignIn.RequireConfirmedAccount = true)
.AddEntityFrameworkStores<ApplicationDbContext>();
builder.Services.Configure<IISServerOptions>(options =>
{
options.AutomaticAuthentication = false;
});
builder.Services.AddTransient<IClaimsTransformation, MyClaimsTransformation>();
builder.Services.AddAuthentication(IISServerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme);
builder.Services.AddRazorPages();
var app = builder.Build();
if (app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseMigrationsEndPoint();
}
else
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error");
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthentication();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapRazorPages();
app.Run();
| Option | Default | Setting |
|---|---|---|
AutomaticAuthentication |
true |
If true, IIS Server sets the HttpContext.User authenticated by Windows Authentication. If false, the server only provides an identity for HttpContext.User and responds to challenges when explicitly requested by the AuthenticationScheme. Windows Authentication must be enabled in IIS for AutomaticAuthentication to function. For more information, see Windows Authentication. |
AuthenticationDisplayName |
null |
Sets the display name shown to users on login pages. |
AllowSynchronousIO |
false |
Whether synchronous I/O is allowed for the HttpContext.Request and the HttpContext.Response. |
MaxRequestBodySize |
30000000 |
Gets or sets the max request body size for the HttpRequest. Note that IIS itself has the limit maxAllowedContentLength which will be processed before the MaxRequestBodySize set in the IISServerOptions. Changing the MaxRequestBodySize won't affect the maxAllowedContentLength. To increase maxAllowedContentLength, add an entry in the web.config to set maxAllowedContentLength to a higher value. For more details, see Configuration. |
Differences between in-process and out-of-process hosting
-
IIS HTTP Server (IISHttpServer) is used instead of Kestrel server. For in-process,
CreateDefaultBuildercalls UseIIS to:-
Register the
IISHttpServer. -
Configure the port and base path the server should listen on when running behind the ASP.NET Core Module.
-
Configure the host to capture startup errors.
-
-
The
requestTimeoutattribute doesn't apply to in-process hosting. -
Sharing an app pool among apps isn't supported. Use one app pool per app.
-
The architecture (bitness) of the app and installed runtime (x64 or x86) must match the architecture of the app pool. For example, apps published for 32-bit (x86) must have 32-bit enabled for their IIS Application Pools. For more information, see the Create the IIS site section.
-
Client disconnects are detected. The
HttpContext.RequestAbortedcancellation token is cancelled when the client disconnects. -
When hosting in-process,
AuthenticateAsyncisn't called internally to initialize a user. Therefore, anIClaimsTransformationimplementation used to transform claims after every authentication isn't activated by default. When transforming claims with anIClaimsTransformationimplementation, callAddAuthenticationto add authentication services:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Server.IIS;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using RPauth.Data;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
var connectionString = builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection");
builder.Services.AddDbContext<ApplicationDbContext>(options =>
options.UseSqlServer(connectionString));
builder.Services.AddDatabaseDeveloperPageExceptionFilter();
builder.Services.AddDefaultIdentity<IdentityUser>(options => options.SignIn.RequireConfirmedAccount = true)
.AddEntityFrameworkStores<ApplicationDbContext>();
builder.Services.Configure<IISServerOptions>(options =>
{
options.AutomaticAuthentication = false;
});
builder.Services.AddTransient<IClaimsTransformation, MyClaimsTransformation>();
builder.Services.AddAuthentication(IISServerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme);
builder.Services.AddRazorPages();
var app = builder.Build();
if (app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseMigrationsEndPoint();
}
else
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error");
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthentication();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapRazorPages();
app.Run();
- Web Package (single-file) deployments aren't supported.