Parallel programming - Overview
In this article
In this tutorial, we'll look at how to parallelize your code to distribute work across multiple processors.
Visual Studio and .NET simplify parallel programming by providing a runtime, class library types, and diagnostic tools. Visual Studio and .NET enhance support for parallel programming by providing a runtime, class library types, and diagnostic tools.
The following illustration provides a high-level overview of the parallel programming architecture in .NET.
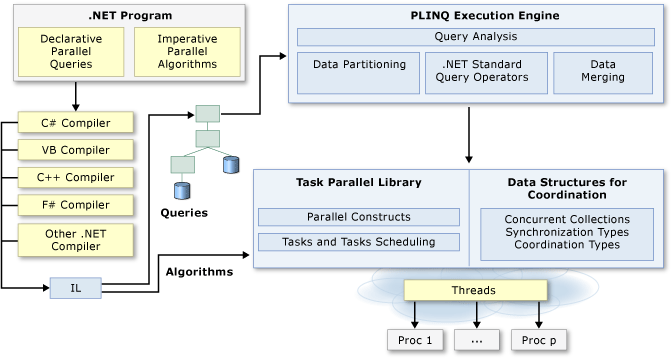
Related Topics
| Technology | Description |
|---|---|
| Task Parallel Library (TPL) | Provides documentation for the System.Threading.Tasks.Parallel class, which includes parallel versions of For and ForEach loops, and also for the System.Threading.Tasks.Task class, which represents the preferred way to express asynchronous operations. |
| Parallel LINQ (PLINQ) | A parallel implementation of LINQ to Objects that significantly improves performance in many scenarios. |
| Data Structures for Parallel Programming | Provides links to documentation for thread-safe collection classes, lightweight synchronization types, and types for lazy initialization. |
| Parallel Diagnostic Tools | Provides links to documentation for Visual Studio debugger windows for tasks and parallel stacks, and for the Concurrency Visualizer. |
| Custom Partitioners for PLINQ and TPL | Describes how partitioners work and how to configure the default partitioners or create a new partitioner. |
| Task Schedulers | Describes how schedulers work and how the default schedulers may be configured. |
| Lambda Expressions in PLINQ and TPL | Provides a brief overview of lambda expressions in C# and Visual Basic, and shows how they are used in PLINQ and the Task Parallel Library. |
| For Further Reading | Provides links to additional information and sample resources for parallel programming in .NET. |
See also
-
Managed Threading
-
Asynchronous programming patterns
Ref: Parallel programming in .NET: A guide to the documentation